Cheque Bounce Charges, Meaning and How to Handle It

What is a Cheque Bounce Case?
- Check bounce meaning: A cheque bounce case occurs when a cheque issued by a drawer is returned by the bank unpaid due to insufficient funds, a mismatched signature, or other reasons. This can lead to legal consequences under Section 138 of the Negotiable Instruments Act, of 1881.
Dishonoured Cheque
- A dishonored cheque is another term for a bounced cheque. It means the bank has refused to honor the cheque due to various reasons such as insufficient funds, account closure, or a mismatched signature.
Cheque Bounce Charges
- When a cheque bounces, both the payer and the payee may incur charges from their respective banks. These charges vary depending on the bank and the amount involved.
| Bank | Local Cheque Deposited by Customer | Cheque Issued by Customer | Outstation Cheque Deposited by Customer | Cheque Returned for Insufficient Funds | Cheque Returned for Technical Reasons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State Bank of India (SBI) | ₹150 + GST for cheques up to ₹1 lakh, ₹250 + GST for cheques above ₹1 lakh | ₹500 + GST | ₹150 + GST | ₹500 + GST | ₹150 + GST |
| Punjab National Bank (PNB) | Varies | Varies | Varies | Varies | Varies |
| Bank of Baroda (BoB) | ₹100 per cheque | ₹350 for first return, ₹750 for subsequent returns | ₹150 + other bank charges | ₹350 | ₹50 (except for signature verification) |
| ICICI Bank | ₹100 per cheque | ₹350 for first return, ₹750 for subsequent returns | ₹150 + other bank charges | ₹350 | ₹50 (except for signature verification) |
| HDFC Bank | ₹350 | ₹400 for non-maintenance of average quarterly balance | ₹75 | ₹100 per instance | No charge |
| Axis Bank | ₹100 per cheque | ₹350 for first return, ₹750 for subsequent returns | ₹150 + other bank charges | ₹350 | ₹50 (except for signature verification) |
| Kotak Mahindra Bank | ₹100 per cheque | ₹350 for first return, ₹750 for subsequent returns | ₹150 + other bank charges | ₹350 | ₹50 (except for signature verification) |
| Federal Bank | ₹100 per cheque | ₹350 for first return, ₹750 for subsequent returns | ₹150 + other bank charges | ₹350 | ₹50 (except for signature verification) |
| IndusInd Bank | ₹100 per cheque | ₹350 for first return, ₹750 for subsequent returns | ₹150 + other bank charges | ₹350 | ₹50 (except for signature verification) |
| Yes Bank | ₹100 per cheque | ₹350 for first return, ₹750 for subsequent returns | ₹150 + other bank charges | ₹350 | ₹50 (except for signature verification) |
Please note that these charges are subject to change and may vary based on the specific policies of each bank. It's always a good idea to check directly with your bank for the most accurate and up-to-date information.
Advice Not Received Cheque Return Meaning
- This term refers to a situation where the cheque return memo does not provide any specific reason for the cheque being dishonored. It simply states that the cheque was returned without any advice or explanation.
Post-Dated Cheque Meaning
- A post-dated cheque is dated for a future date. Presenting such a cheque before the specified date can lead to its dishonor.
Stale Cheque Meaning
- A cheque becomes stale if it is not presented for payment within six months from the date of issue. Banks usually refuse to honor stale cheques.
Cheque Number on Cheque
- The cheque number is a unique identifier assigned to each cheque issued by a bank. It helps in tracking and referencing the cheque during transactions.
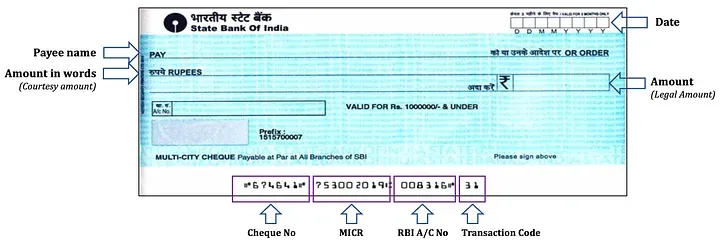
Other Bank Cheque Clearing Time
- Different banks have varying cheque clearing times, typically ranging from 3 to 7 business days. It is important to be aware of these timelines to avoid any delays.
Cheque Bounce Punishment
The punishment for cheque bounce is outlined under Section 138 of the Negotiable Instruments Act, of 1881. Here are the key points:
- Imprisonment: The drawer can be sentenced to imprisonment for a term that may extend to two years.
- Fine: The drawer may be fined an amount that can be up to twice the amount of the cheque.
- Both: In some cases, the drawer may face both imprisonment and a fine.
Additionally, the court may order the drawer to pay compensation to the payee, which is usually the cheque amount plus any additional charges incurred due to the bounced cheque.
It's important to maintain sufficient funds in your account and ensure that all details on the cheque are correct to avoid such legal consequences.
FAQs:
What happens if a cheque bounces?
- Under Section 138 of the Negotiable Instruments Act, of 1881, the punishment for a cheque bounce can include imprisonment for a term of up to two years or a fine that may be up to twice the amount of the cheque, or both. Additionally, the payee has the right to file a civil suit against the issuer (drawer) to recover the cheque amount. This legal provision ensures that the person who has issued the bounced cheque is held accountable, providing both criminal and civil recourse for the payee.
What is the new rule of cheque bounce?
In India, dishonoring a cheque is considered a criminal offense under Section 138 of the Negotiable Instruments Act, of 1881. If a cheque bounces, the drawer can face one of the following penalties:
- Fine: The offender may be required to pay a fine, which can be up to twice the amount of the bounced cheque.
- Imprisonment: The drawer may be sentenced to imprisonment for up to 2 years.
Can we file an FIR against cheque bounce?
- Yes, in addition to filing a complaint under Section 138 of the Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881, you can also file an FIR under Sections 406 (Criminal Breach of Trust) or 420 (Cheating) of the Indian Penal Code (IPC) if there is a criminal element involved, such as fraud or deliberate dishonesty by the drawer. These sections provide for additional criminal action when there is intent to deceive or misappropriate funds. Pursuing this route can lead to more severe penalties, including potential imprisonment if proven.
How much penalty for a cheque bounce?
If a cheque bounces due to insufficient funds, the drawer can be held criminally liable under Section 138 of the Negotiable Instruments Act, of 1881. The penalties include:
- Fine: The court can impose a fine up to twice the amount of the cheque.
- Imprisonment: The drawer can face imprisonment for a term of up to two years.
- Both: In some cases, the court may impose both a fine and imprisonment.
Additionally, the payee can pursue a civil suit to recover the amount on the cheque, allowing for both criminal and civil remedies against the drawer.
What is the legal action for a bounced Cheque?
- Section 138 of the Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881 declares cheque bounce as a punishable offence. If a cheque is dishonored, the drawer may face the following penalties:
- A fine of up to double the value of the cheque.
- Imprisonment for a period of up to two years.
- In some cases, both fines and imprisonment can be imposed.
This legal provision aims to deter individuals from issuing cheques without maintaining sufficient funds or engaging in fraudulent activities.
What should I do immediately after receiving a cheque bounce notification?
- Upon receiving a cheque bounce notification, immediately contact your bank to understand the reason, inform the issuer of the resolution, and explore if re-submission or alternative payment methods are feasible.
How long do I have to respond to a cheque bounce notice legally?
- Legally, you have 30 days to respond to a cheque bounce notice from the date of receipt, either by making the payment or communicating with the issuer to resolve the matter.
Can a cheque bounce case affect my credit score?
- Yes, a cheque bounce case can affect your credit score, especially if it leads to legal action or is reported by the bank. This can impact your ability to secure loans or credit in the future.
What are the common reasons for a cheque to bounce?
- Common reasons for a cheque to bounce include insufficient funds in the account, mismatched signatures, account closure, post-dated or stale-dated cheques, overwriting without authorization, and discrepancies in the cheque details.
Is it possible to settle a cheque bounce case out of court?
- Yes, it is possible to settle a cheque bounce case out of court through negotiation between the involved parties. The drawer can offer to pay the due amount along with any applicable charges to the payee to avoid legal proceedings.
How can I avoid cheque bounces in the future?
- To avoid cheque bounces in the future, ensure sufficient funds are in your account before issuing a cheque, regularly monitor your account balance, avoid making errors on the cheque, keep track of post-dated cheques issued, and use alternative payment methods when possible.
How to Fill Cheque Deposit Slip
- To fill out a cheque deposit slip, you need to provide details such as the cheque number, amount, date, and account number. Ensure all information is accurate to avoid any issues.
How to Escape from Cheque Bounce Case?
- To avoid legal consequences, it is crucial to maintain sufficient funds in your account, ensure correct signatures, and avoid issuing post-dated or stale cheques. If a cheque bounces, promptly resolve the issue by depositing the required amount.
Please follow us on our social site and YouTube and subscribe to our website.
Manage your business cash flows and payable/receivables using our Bahi Khata App.




Comments ()