Introduction:
- Open Banking is a revolutionary concept transforming the financial industry by fostering increased competition, innovation, and transparency. It involves the use of open APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that enable third-party developers to build applications and services around financial institutions. This new model is reshaping how consumers interact with their finances and how financial institutions operate. In this article, we will explore the definition of Open Banking, how it works, its benefits, and its associated risks.
Definition of Open Banking:
- Open Banking refers to the practice of allowing third-party financial service providers to access consumer banking, transaction, and other financial data from banks and other financial institutions through APIs(Application Programming Interfaces). This is done with the explicit consent of the consumer. The concept aims to create a more integrated and efficient financial ecosystem by facilitating the seamless exchange of financial information.
- Open Banking is part of a broader movement towards greater transparency and consumer empowerment in the financial services sector. It is underpinned by regulatory frameworks like the European Union's Payment Services Directive 2 (PSD2) and the UK's Open Banking initiative, which mandate that banks must provide secure access to customer data to approved third parties.
How Open Banking Works:
Open Banking works through a secure and regulated process involving multiple stakeholders:
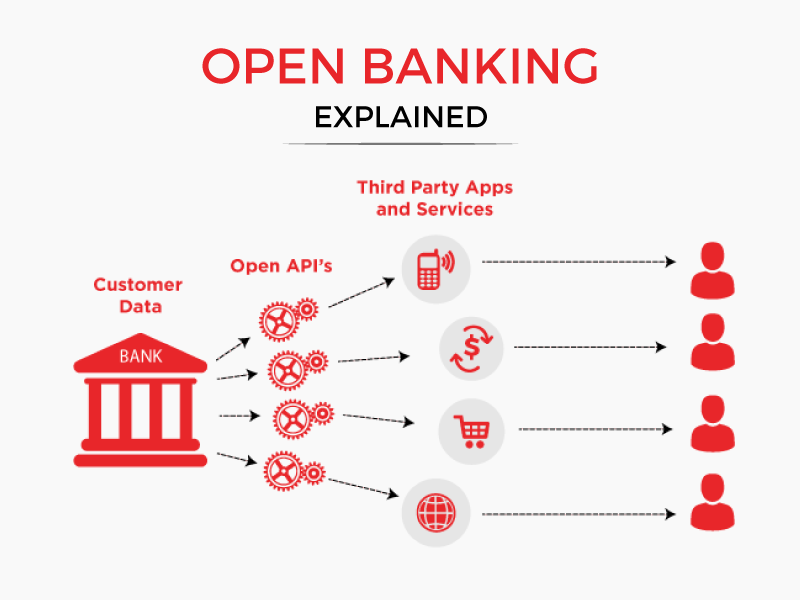
- APIs: Banks and financial institutions create APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that allow third-party providers (TPPs) to access financial data. These APIs are designed to ensure security and protect consumer data.
- Consumer Consent: Consumers must provide explicit consent for their data to be shared. This typically involves a consent flow where the consumer authorizes access through a secure authentication process.
- Third-Party Providers (TPPs): TPPs use the APIs to access consumer data and offer various financial services, such as budgeting tools, payment services, and personalized financial advice.
- Regulation and Compliance: Regulatory bodies oversee Open Banking practices to ensure data privacy, security, and compliance with relevant laws. This includes monitoring how data is accessed and used.
Benefits of Open Banking:
Open Banking offers numerous benefits for consumers, financial institutions, and the broader financial ecosystem:
- Enhanced Consumer Experience: Open Banking allows for the development of innovative financial products and services that cater to individual needs. Consumers can benefit from personalized financial advice, improved budgeting tools, and seamless payment solutions.
- Increased Competition: By lowering barriers to entry for new financial service providers, Open Banking fosters competition. This can lead to better services and lower costs for consumers as banks and TPPs strive to offer superior products.
- Financial Inclusion: Open Banking can help reach underserved populations by enabling fintech companies to offer alternative financial services that cater to those without access to traditional banking.
- Improved Transparency and Control: Consumers gain greater control over their financial data and can choose who they share it with. This increased transparency can lead to more informed financial decisions.
- Innovation: Open Banking encourages innovation within the financial sector by allowing fintech companies to create new services that integrate seamlessly with existing banking infrastructure. This can lead to the development of cutting-edge financial technologies.
Risks Associated with Open Banking
While Open Banking offers significant benefits, it also presents certain risks that need to be managed:
- Data Privacy and Security: The primary concern with Open Banking is the security of consumer data. Ensuring that APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) and third-party providers adhere to stringent security standards is crucial to prevent data breaches and misuse.
- Regulatory Compliance: As Open Banking is regulated differently across various jurisdictions, ensuring compliance with all relevant laws can be challenging. Financial institutions and TPPs must navigate a complex regulatory landscape to avoid legal issues.
- Consumer Awareness and Trust: For Open Banking to succeed, consumers must trust that their data will be handled securely and used responsibly. Building this trust requires transparency from both banks and TPPs about how data is used and protected.
- Technical Challenges: Implementing and maintaining secure and efficient APIs can be technically challenging for banks. They must ensure that their systems are robust enough to handle the increased data traffic and interactions with TPPs.
- Market Dynamics: Increased competition can lead to market fragmentation, where too many small players may struggle to sustain themselves. This could potentially result in market instability.
Conclusion:
- In conclusion, Open Banking represents a significant shift in the financial landscape, promising enhanced services and increased competition while also posing challenges related to data security and regulatory compliance. As the financial industry continues to evolve, Open Banking will likely play a crucial role in shaping the future of financial services.
FAQs about Open Banking
Who invented open banking?
- Though few households installed the system, the interface was used through 2005, and Deutsche Bundespost is credited with initiating the open banking movement. In 1998, Germany developed another open banking and customer self-service interface.
What is Open Banking?
- Open Banking is the practice of allowing third-party financial service providers to access consumer financial data from banks and other financial institutions through secure APIs, with the consumer's consent.
What is the concept of open banking?
- Open banking uses APIs to share financial data with third parties, who then provide apps or services to bank customers using this data.
What is the idea of open banking?
- Open banking is a framework that allows you to share your financial data with fintech companies of your choice through secure online channels.
Why is open banking so important?
- Open banking enables customers to share their financial data with third-party providers, allowing access to a wider range of products and services, and helps customers save money on loans and mortgages.
What is the principle of open banking?
- Open banking is all about data. Users consent to third parties accessing their data to offer tailored services or products. Ethical access, use, and sharing of data are critical to the success of open banking and open finance ecosystems.
How does Open Banking benefit consumers?
- Consumers benefit from personalized financial services, improved budgeting tools, lower costs, enhanced transparency, and greater control over their financial data.
Are there risks associated with Open Banking?
- Yes, risks include data privacy and security concerns, regulatory compliance challenges, the need for consumer trust, technical challenges, and potential market fragmentation.
How do consumers grant consent in Open Banking?
- Consumers typically grant consent through a secure authentication process, often involving multi-factor authentication, to authorize third-party providers to access their data.
What role do APIs play in Open Banking?
- APIs are the technical foundation of Open Banking, enabling secure and standardized data sharing between banks and third-party providers.
How does Open Banking foster innovation?
- Open Banking encourages innovation by allowing fintech companies to develop new financial services that integrate with existing banking infrastructure, leading to the creation of advanced financial technologies.
What regulations govern Open Banking?
- Regulations like the European Union's PSD2 and the UK's Open Banking initiative govern Open Banking practices, ensuring data privacy, security, and compliance with relevant laws.
Can Open Banking improve financial inclusion?
- Yes, Open Banking can improve financial inclusion by enabling fintech companies to offer services to underserved populations, providing alternatives to traditional banking.
What technical challenges do banks face with Open Banking?
- Banks face challenges in implementing and maintaining secure and efficient APIs, ensuring their systems can handle increased data traffic, and integrating with various third-party providers.
How can consumers ensure their data is safe with Open Banking?
- Consumers should choose reputable third-party providers, stay informed about how their data is used, and take advantage of security features like multi-factor authentication to protect their information.
We hope that you like this content and for more such content Please follow us on our social site and YouTube and subscribe to our website.
Manage your business cash flows and payable/receivables using our Bahi Khata App


